- Home
- About us
- Products
- Lab fermenter(SS316, 5L-50L)
- Industry fermenter(1KL-400KL)
- Mammalian cell bioreactor(5L-10KL)
- Lab Fermenter Bioreactor Industrial Stainless Steel Fermenter
- Vaccine Fermenter(GMP) Fermentation Equipment stainless Steel Bioreactor
- Mini Lab Glass Fermenter Magnetic Mixing Cell Culture Fermenter Bioreactor
- CIP Station Automatic Bioreactor Fermenter
- Faqs
- News
- Certificate
- Contact us
Insights into Lab Scale Fermenters, Industrial Fermentadoras, and Syngas Fermentors
Question 1: What are the key features of a lab scale fermenter?
A lab scale fermenter is typically characterized by its smaller size, precise control over parameters such as temperature, pH, and dissolved oxygen, and the ability to conduct experiments under controlled and reproducible conditions. It often comes with advanced monitoring and data logging systems to facilitate detailed analysis of the fermentation process.
Question 2: How does an industrial fermentadora differ from a lab scale one?
Industrial fermentadoras are larger in size and designed for high-volume production. They are built to handle continuous operation, have more robust construction for durability, and may incorporate automated control systems for efficient and consistent performance.
Question 3: What is a syngas fermentor and how does it work?
A syngas fermentor is a specialized type of fermentor that utilizes syngas (a mixture of carbon monoxide, hydrogen, and carbon dioxide) as the substrate for microbial growth and metabolite production. The microorganisms in the fermentor have the ability to metabolize these gases to produce valuable products such as alcohols or organic acids.
Question 4: What types of microorganisms are commonly used in syngas fermentors?
Some common microorganisms used in syngas fermentors include species of Clostridium, Butyribacterium, and Moorella. These organisms have adapted to utilize the components of syngas as their energy and carbon sources.
Question 5: How is the quality and purity of the final product ensured in a lab scale fermenter?
In a lab scale fermenter, this is achieved through careful monitoring of the process parameters, frequent sampling and analysis of the culture broth, and strict adherence to aseptic techniques to prevent contamination.
Question 6: What challenges are associated with scaling up from a lab scale fermenter to an industrial fermentadora?
Scaling up presents challenges such as maintaining uniform mixing, heat transfer, and mass transfer across the larger volume. Changes in fluid dynamics and the need for more efficient sterilization and process control systems also need to be addressed.
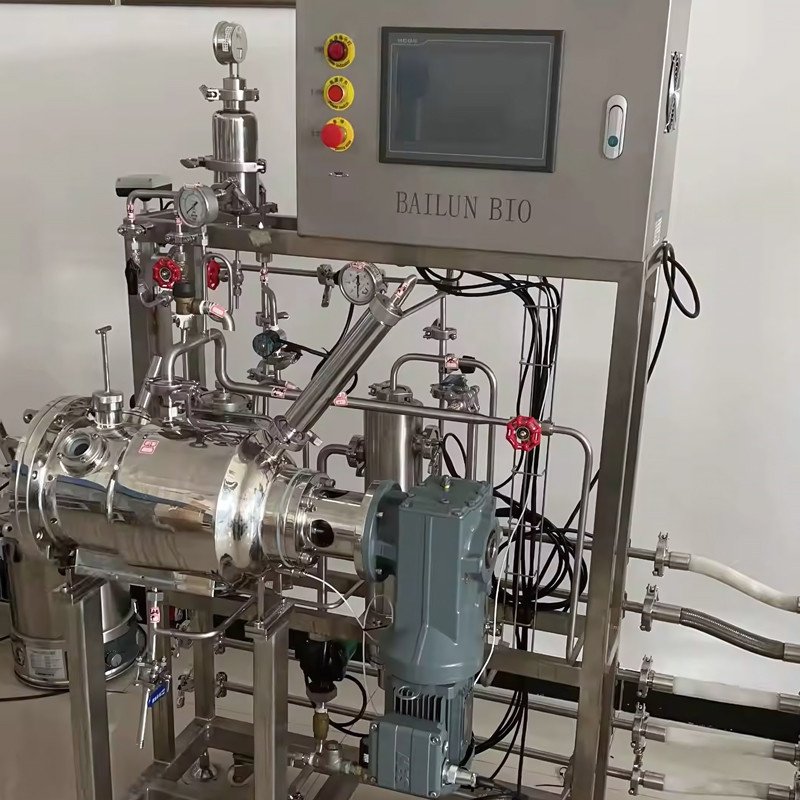
Question 7: Can the same microorganisms be used in both lab scale and industrial fermentors?
Often, the same microorganisms can be used, but their performance and requirements may differ due to the variations in scale and operating conditions. Optimization and adaptation of the microbial strains may be necessary for industrial-scale applications.
Question 8: How is the syngas composition optimized for efficient fermentation in a syngas fermentor?
The syngas composition can be optimized by adjusting the ratios of the component gases based on the metabolic capabilities of the microorganisms and the desired products. Additionally, pretreatment of the syngas to remove impurities can enhance the fermentation process.
Question 9: What safety precautions should be taken when operating a lab scale fermenter?
Safety precautions include proper training in handling equipment and chemicals, wearing appropriate personal protective equipment, ensuring electrical safety, and following established protocols for handling potentially hazardous substances and microorganisms.
Question 10: How is the performance of a syngas fermentor evaluated?
The performance is evaluated based on parameters such as the rate of syngas consumption, the yield and productivity of the desired products, the stability of the microbial culture, and the overall energy efficiency of the process.

