- Home
- About us
- Products
- Lab fermenter(SS316, 5L-50L)
- Industry fermenter(1KL-400KL)
- Mammalian cell bioreactor(5L-10KL)
- Lab Fermenter Bioreactor Industrial Stainless Steel Fermenter
- Vaccine Fermenter(GMP) Fermentation Equipment stainless Steel Bioreactor
- Mini Lab Glass Fermenter Magnetic Mixing Cell Culture Fermenter Bioreactor
- CIP Station Automatic Bioreactor Fermenter
- Faqs
- News
- Certificate
- Contact us
Heavy weight! The next billion dollar trend, advanced biotechnology technology
time2024/11/02
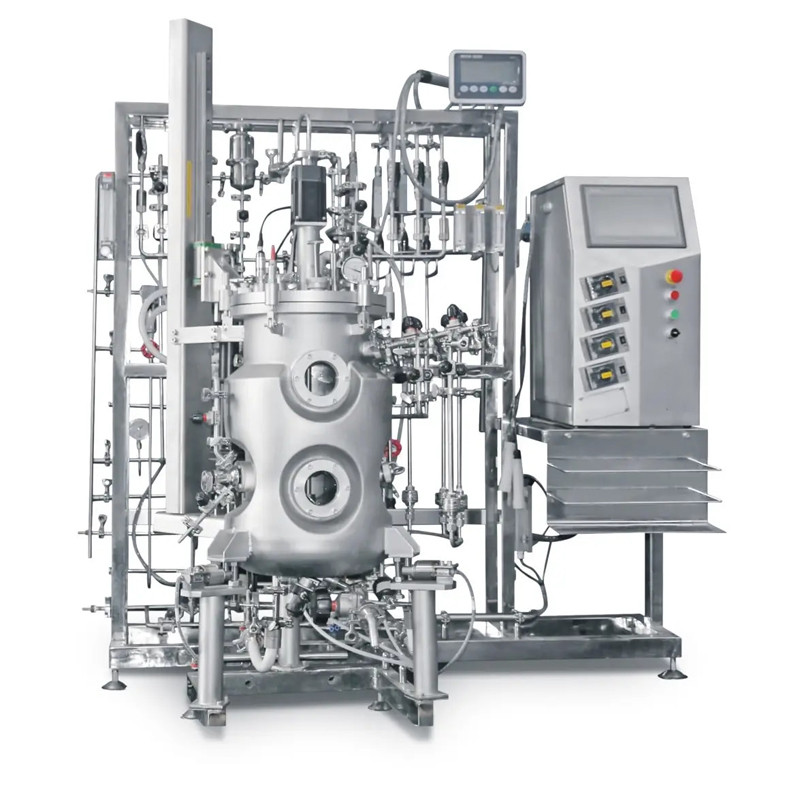

- From the date of the announcement, foreign-invested enterprises are allowed to engage in the development and application of human stem cell and gene diagnosis and treatment technologies in China
From the date of the announcement, foreign-invested enterprises are allowed to engage in the development and application of human stem cell and gene diagnosis and treatment technologies in China (Beijing), China (Shanghai), China (Guangdong) Pilot Free Trade Zone, and Hainan Free Trade Port. These products can be used nationwide after registration and approval for production.
Notice from the Ministry of Commerce, National Health Commission, and National Medical Products Administration on Launching Pilot Projects to Expand Openness in the Medical Field
Commercial Letter [2024] No. 568
The competent authorities for commerce, health, human genetic resources, and drug supervision and management in Beijing, Tianjin, Shanghai, Jiangsu, Fujian, Guangdong, and Hainan provinces:
In order to implement the decision and deployment of the Third Plenary Session of the 20th Central Committee of the Communist Party of China on expanding independent opening up, introduce foreign investment to promote high-quality development in China's medical related fields, and better meet the medical and health needs of the people, it is planned to carry out pilot work on expanding opening up in the medical field. The relevant matters are hereby notified as follows
In the field of biotechnology.
From the date of issuance of this notice, foreign-invested enterprises are allowed to engage in the development and application of human stem cell, gene diagnosis and treatment technologies in the China (Beijing) Pilot Free Trade Zone, China (Shanghai) Pilot Free Trade Zone, China (Guangdong) Pilot Free Trade Zone, and Hainan Free Trade Port for product registration, listing, and production. All products that have been registered, marketed, and approved for production can be used nationwide. Foreign invested enterprises planning to pilot projects should comply with relevant laws, administrative regulations and other provisions of China, meet the requirements of human genetic resource management, drug clinical trials (including international multicenter clinical trials), drug registration and marketing, drug production, ethical review and other regulations, and fulfill relevant management procedures.
2、 Sole proprietorship hospital field
We plan to allow the establishment of wholly foreign-owned hospitals in Beijing, Tianjin, Shanghai, Nanjing, Suzhou, Fuzhou, Guangzhou, Shenzhen, and Hainan (excluding traditional Chinese medicine hospitals, excluding mergers and acquisitions of public hospitals). The specific conditions, requirements, and procedures for establishing a wholly foreign-owned hospital will be notified separately.
The competent departments in charge of commerce, health, human genetic resources, and drug supervision and management in pilot areas should, according to their respective responsibilities, increase policy promotion efforts, actively connect with willing foreign-invested enterprises, and strengthen services; At the same time, it is necessary to strengthen interdepartmental consultations and implement supervision and management of pilot enterprises within their respective responsibilities in accordance with the law, timely identify and effectively prevent risks, promote the pilot work of expanding the opening up of biotechnology and wholly-owned hospitals, and ensure the effectiveness of the pilot work
For any questions encountered during the pilot process, please contact the Ministry of Commerce, the National Health Commission, and the National Medical Products Administration in a timely manner.

The implementation of this policy is expected to promote the high-quality development of China's biopharmaceutical industry, meet the medical and health needs of the people, and attract more foreign investment into China's medical field.
At the same time, the policy also plans to allow the establishment of wholly foreign-owned hospitals in Beijing, Tianjin, Shanghai, Nanjing, Suzhou, Fuzhou, Guangzhou, Shenzhen, and the entire island of Hainan (excluding traditional Chinese medicine, excluding mergers and acquisitions of public hospitals).
The editor believes that in the next 20 years, China's biomedical industry will usher in huge development opportunities. This is mainly based on two factors:
The demand growth brought about by demographic changes: China experienced significant population growth after 1949, and this group of people entered old age over time. With the growth of age and the improvement of health awareness, especially in the context of the COVID-19 epidemic, the demand for biotechnology and medical services will increase significantly.
Active participation in the capital market: For a long time, the investment of US dollar capital in China has mainly focused on areas that can obtain high valuations in the US market. Biotechnology has become an important field for attracting foreign investment due to its high growth potential and innovation.
Heavy weight! Nature: Chinese scientists propose a new paradigm of 'quantitative synthetic biology', moving from trial and error to precise prediction, using innovative methods that are automated, high-throughput, and standardized.

In the future, the policy of opening up foreign investment will have a huge impact on Chinese biopharmaceutical companies
One is the intensification of market competition: the entry of foreign hospitals and biotechnology enterprises will enhance the competitiveness of China's medical market.
Domestic biopharmaceutical companies will face direct competition from international advanced enterprises and technologies, which may force local enterprises to accelerate technological innovation and improve service quality to maintain their market position.
The second is the introduction of technology and management experience: foreign-funded enterprises usually have advanced technology and management experience, and their entry helps to improve the overall level of China's biopharmaceutical industry.
Domestic enterprises can enhance their research and development capabilities and market competitiveness by collaborating, learning, or introducing technology and management experience from foreign-funded enterprises.
The third is capital and cooperation opportunities: the opening up of foreign investment may bring more capital inflows, providing financial support and cooperation opportunities for domestic biopharmaceutical enterprises. This helps companies expand their scale, accelerate research and development processes, and expand their markets.
Fourthly, talent mobility and cultivation: The entry of foreign-funded enterprises may attract and cultivate more high-end talents, while also exacerbating talent mobility. Domestic enterprises need to strengthen talent cultivation and incentive mechanisms to retain key talents and attract new talents to join.