- Home
- About us
- Products
- Lab fermenter(SS316, 5L-50L)
- Industry fermenter(1KL-400KL)
- Mammalian cell bioreactor(5L-10KL)
- Lab Fermenter Bioreactor Industrial Stainless Steel Fermenter
- Vaccine Fermenter(GMP) Fermentation Equipment stainless Steel Bioreactor
- Mini Lab Glass Fermenter Magnetic Mixing Cell Culture Fermenter Bioreactor
- CIP Station Automatic Bioreactor Fermenter
- Faqs
- News
- Certificate
- Contact us
What is GMP equipment? What are the common GMP equipment?
time2025/01/09
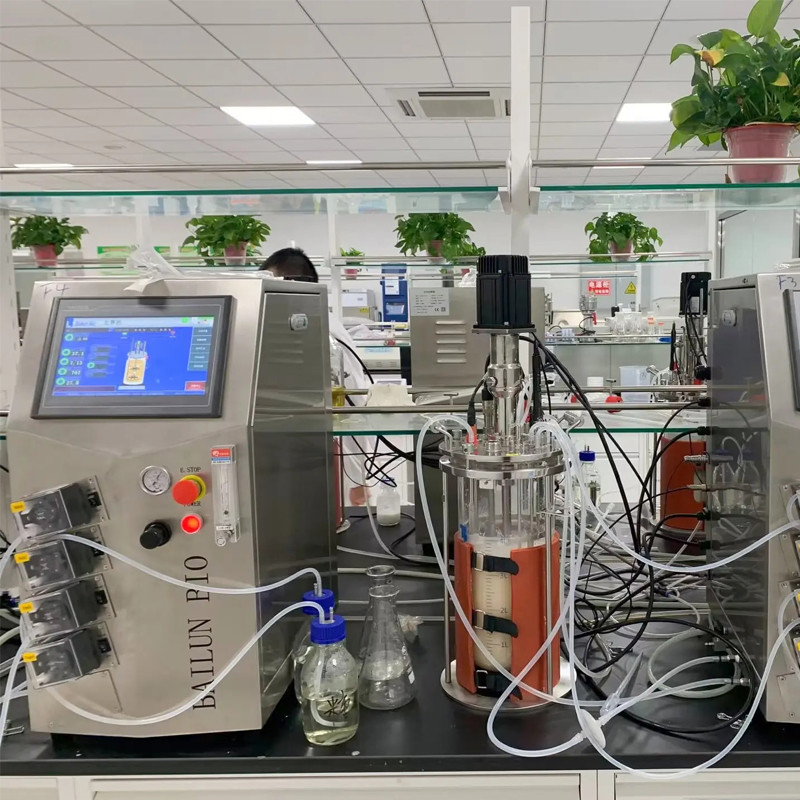

- Equipment refers to devices that comply with the quality management standards for drug production.
Bailun produces and manufactures full process equipment that meets GMP standards

In the biopharmaceutical industry, GMP equipment has strict requirements.
Firstly, GMP equipment should be designed with rationality and scientificity, and its structure should be easy to clean, disinfect, and maintain to prevent contamination of drugs during the production process.
For example, the surface of the equipment should be smooth and free of dead corners to avoid the growth of microorganisms due to material residue.
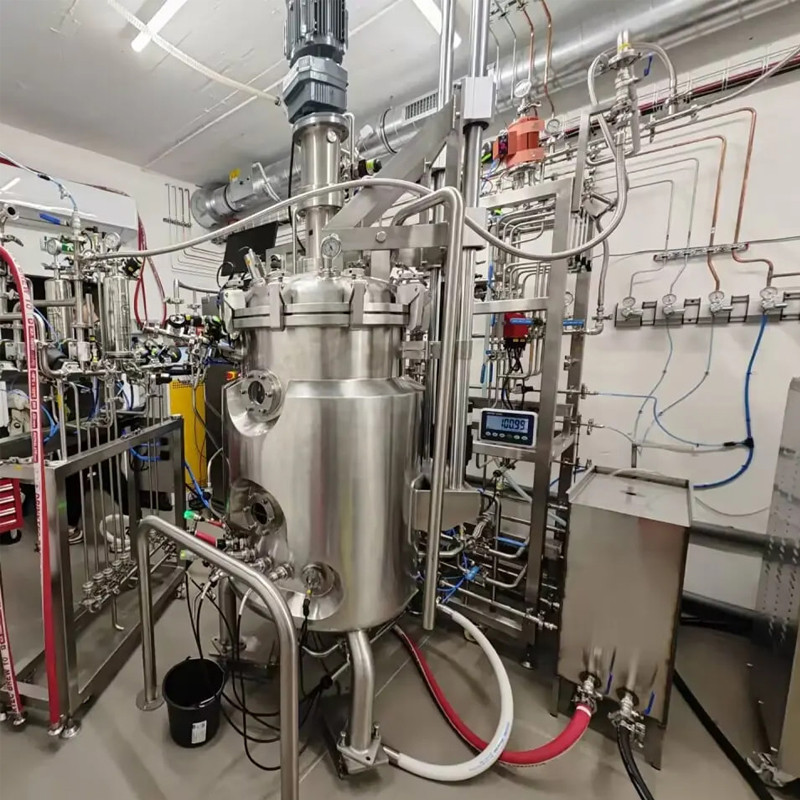

In terms of material selection, non-toxic, corrosion-resistant, and non chemically reactive materials should be used. For example, in the equipment for producing injections, components that come into contact with the drug solution are usually made of materials such as stainless steel that meet pharmaceutical standards.
In terms of installation, GMP equipment should be installed in suitable locations to ensure sufficient spacing between equipment, walls, ceilings, etc., for easy operation, cleaning, and maintenance.
At the same time, it is necessary to ensure that the air circulation and temperature and humidity control in the production environment meet the requirements.
During operation, the equipment should have stability and reliability, and be able to accurately control various parameters such as temperature, pressure, speed, etc., to ensure consistency and repeatability in the drug production process.
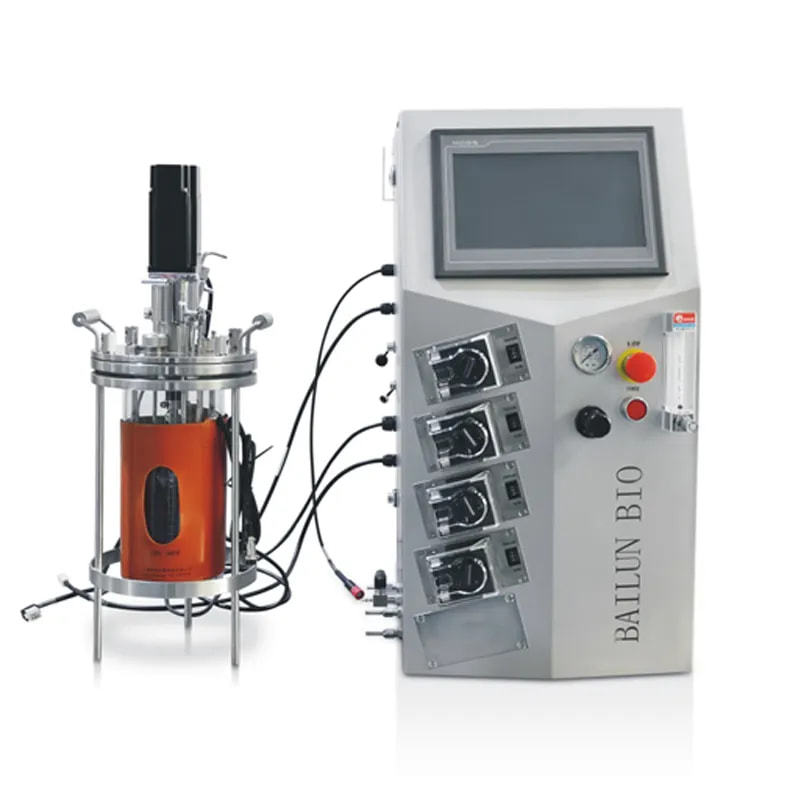

For example, in the bioreactor used for fermentation production of biopharmaceuticals, specific temperatures, pH values, and dissolved oxygen levels can be accurately maintained to ensure stable microbial growth and metabolism, thereby producing qualified drugs in a stable manner.
Validation is an important part of GMP equipment, including installation confirmation (IQ), operational confirmation (OQ), and performance confirmation (PQ).
Through these verification steps, it is demonstrated that the equipment can operate according to predetermined standards and requirements, and continuously produce drugs that meet quality standards.
Only equipment that meets GMP standards can be used for drug research and development, production, and quality control, which plays a key role in ensuring the safety, effectiveness, and quality stability of drugs.
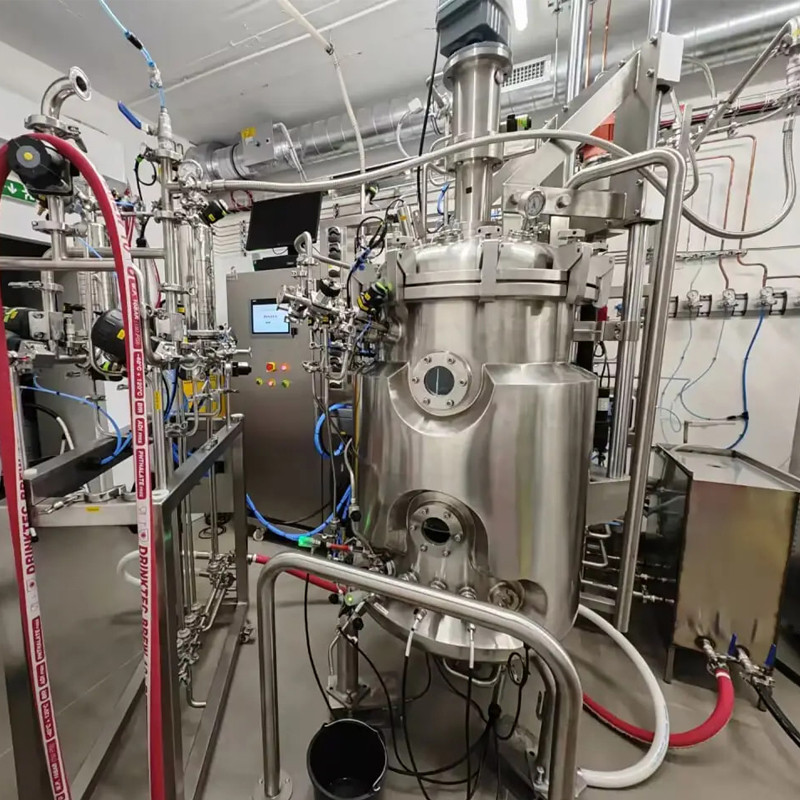

Reactors and bioreactors: In pharmaceutical and chemical production, reactors are used for various chemical reactions, such as esterification and acylation reactions in drug synthesis processes.
Bioreactors are crucial in the field of biopharmaceuticals, such as for cultivating microorganisms or cells to produce biological products such as vaccines and antibodies.
In the process of producing monoclonal antibodies, mammalian cell culture bioreactors require precise control of parameters such as temperature, pH, dissolved oxygen, and stirring speed to provide a suitable environment for cell growth and product expression.
Centrifuge: widely used for solid-liquid separation or separation of liquids with different densities. In antibiotic production, the fermentation broth is processed by a centrifuge to quickly separate bacterial cells from the culture broth, facilitating subsequent product extraction.
The material, speed stability, and sealing performance of the rotor must comply with GMP requirements to prevent material leakage and cross contamination.
Filtering equipment: such as plate and frame filter presses, membrane filters, etc. In the production of injection solutions, membrane filters can effectively remove impurities such as particles and microorganisms from the drug solution, ensuring product clarity and sterility.
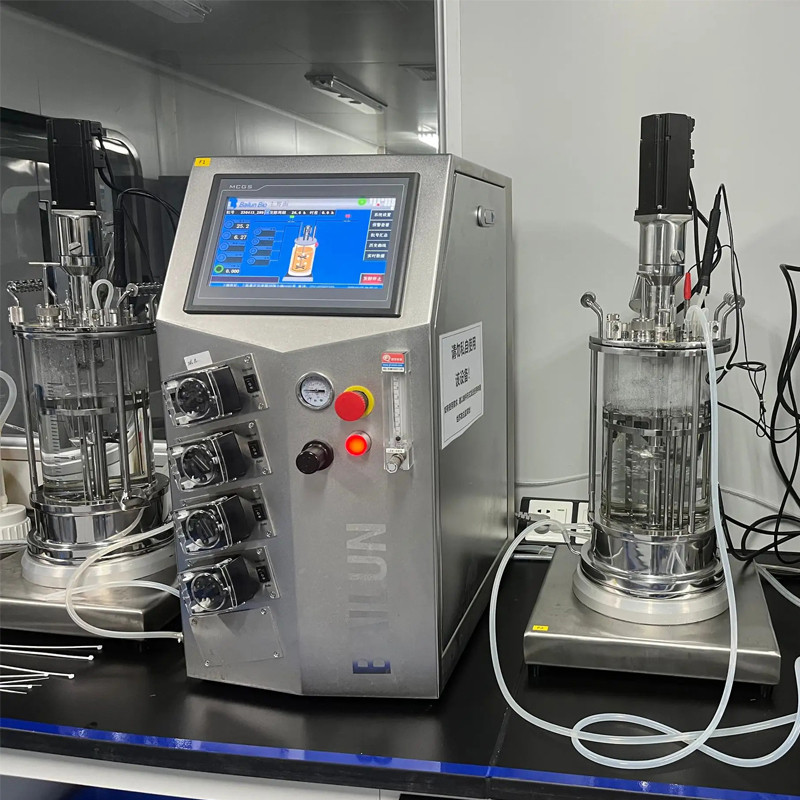

Chromatography equipment: including ion exchange chromatography, gel filtration chromatography, etc., used for the separation and purification of biological macromolecules such as proteins and nucleic acids.
In the production of recombinant protein drugs, ion exchange chromatography can be used to separate proteins based on surface charge differences.
The column material, packing performance, and eluent delivery system of the equipment must ensure accuracy and stability.
Drying equipment: such as spray dryer, vacuum drying oven, etc.
In pharmaceuticals, for some thermosensitive drugs or biological products, such as enzyme preparations, vaccine powder, etc., vacuum drying oven is often used for drying, which has good internal temperature, pressure uniformity and sealing.
Sterilization equipment: In the sterile workshop of pharmaceutical companies, it is used to sterilize culture dishes, pipette tips, work clothes, etc. Its pressure and temperature control system should be precise and reliable to ensure that the specified sterilization conditions are met.